Synonyms: What They Are and How to Use Them to Enrich Your Vocabulary
Victoria | Equipo de redacción
November 4, 2025

Synonyms are one of the most powerful tools in any language. They allow us to express the same idea in different ways, depending on the tone or intention we want to convey. We’ve all been there: repeating the same word over and over in an essay until it sounds flat and boring.
Language shapes the way our ideas are perceived. If we use the same words too often, our writing feels repetitive or dull. But when we learn to vary our vocabulary with synonyms, our texts become more interesting, precise, and dynamic.
Using synonyms not only helps avoid repetition but also shows mastery of the language. For students, it’s an especially useful resource to improve the quality of essays, reports, and presentations. And it doesn’t stop at writing — knowing a variety of synonyms helps you understand academic texts more easily and expand your natural vocabulary.
In this guide, you’ll learn what synonyms are, the types of synonymy, and see a list of common examples you can use to make your writing stand out.

What Is a Synonym?
A synonym is a word that has the same or a very similar meaning as another word, even though it’s spelled and pronounced differently.
We emphasize very similar because synonymy is not always exact — not all words mean the same thing in every context.
Example:
Big and large are often synonyms, but in “a big mistake” and “a large mistake,” only big sounds natural.
In practice, synonyms help us avoid repetition and adjust the tone of what we say or write.
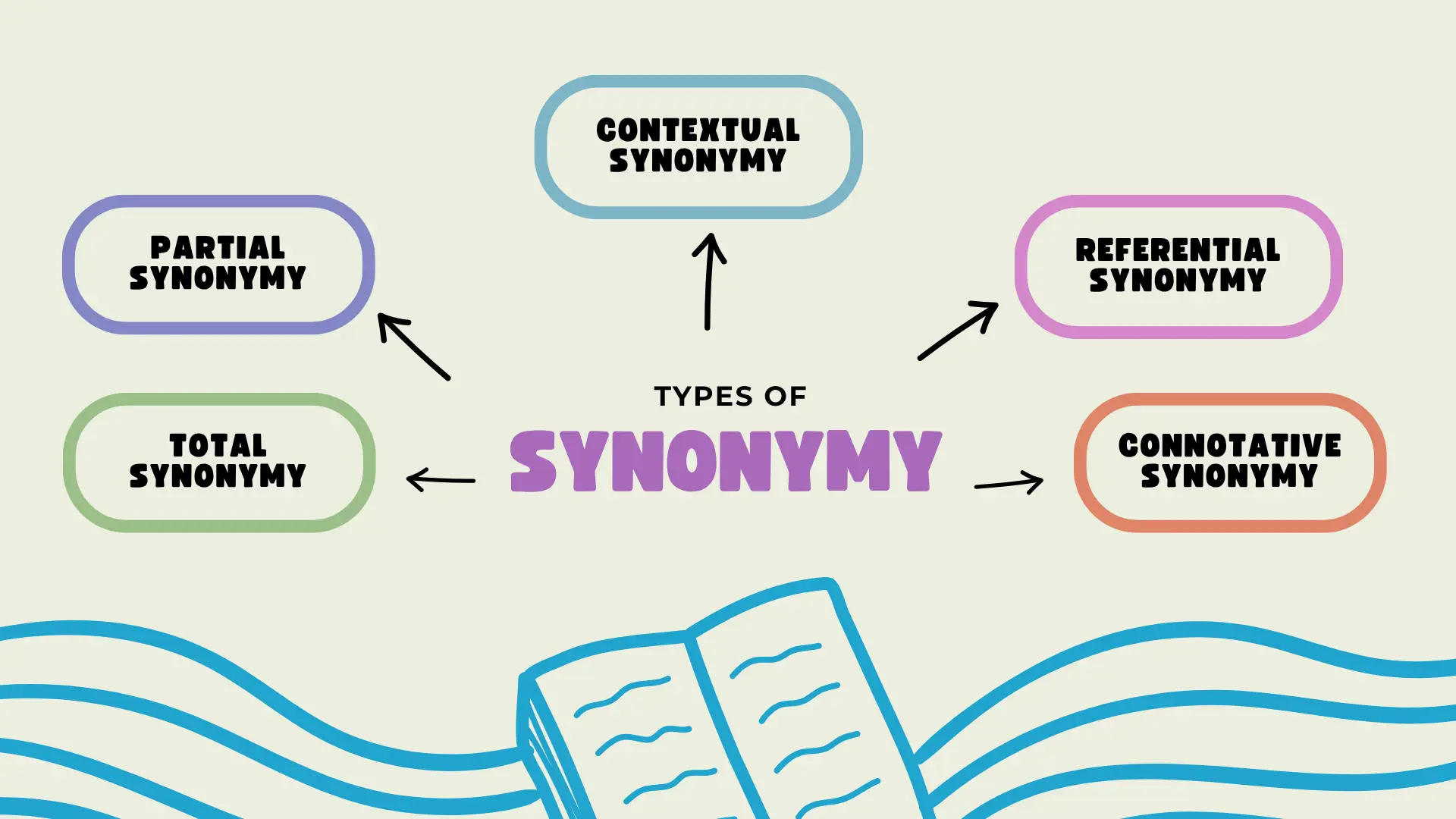
Synonymy
Synonymy is the relationship between two or more words that have similar meanings. However, not all synonyms can be used interchangeably in every situation. That’s why synonymy is classified into different types:
Total synonymy
Occurs when two words can replace each other in any context without changing the meaning.
Examples:
Teacher – instructor
Movie – film
Partial synonymy
Happens when two words share part of their meaning but not in all contexts. This is the most common type of synonymy.
Examples:
Start – begin: “Let’s start the lesson” / “Let’s begin the lesson.” (Both correct)
But: “He made a good start” (you wouldn’t say a good begin).
Contextual synonymy
In this case, the similarity in meaning depends entirely on the context.
Example:
Cold – unfriendly: “She gave me a cold look” / “She gave me an unfriendly look.”
Referential synonymy
Occurs when two words refer to the same object or concept, even if they have different meanings in other contexts.
Example:
Car – automobile: both refer to the same object.
Connotative synonymy
Appears when two words share a similar meaning due to cultural or emotional associations.
Example:
Ambitious – hungry: “He’s hungry for success” (meaning ambitious).
List of Common Synonyms
Beautiful
Pretty, lovely, attractive
Happy
Glad, joyful, pleased
Sad
Unhappy, gloomy, downcast
Fast
Quick, speedy, swift
Slow
Unhurried, sluggish, relaxed
Big
Huge, enormous, gigantic
Small
Tiny, little, miniature
Study
Learn, review, research
Say
Tell, state, express
Brave
Bold, fearless, courageous
Dark
Dim, shadowy, gloomy
Dirty
Messy, filthy, unclean
Clean
Neat, spotless, tidy
Quiet
Silent, calm, peaceful
Help
Assist, support, aid
Important
Significant, crucial, valuable
Ask
Request, inquire, seek
Do
Make, perform, carry out
Work
Job, task, profession
Growth
Progress, development, advancement
Synonyms are more than just similar words — they’re a way to develop language competence, enhance writing, and improve reading comprehension.
Learning to use them correctly helps you express ideas precisely, avoid unnecessary repetition, and give your work a more personal and natural tone.
Knowing multiple synonyms also helps you understand the author’s intention when reading and choose the most accurate word for your own writing. It’s not just about swapping one word for another; it’s about understanding the nuances of meaning and selecting the one that fits your context best.
And if you ever struggle to find the perfect word or want to improve your writing quickly and easily, try our Text Paraphraser at Parafrasist.
This free tool helps you rewrite sentences, find synonyms, and improve clarity in seconds — ideal for students who want to polish their assignments and communicate their ideas more effectively.
Expanding your vocabulary and learning to use synonyms won’t just make you a better writer — it’ll make you a more confident communicator.
Good luck with your studies!